WASHINGTON, May 28 (CGTN) - U.S. President Donald Trump signed an executive order on Thursday he said would limit the ability of social media companies to censor content.
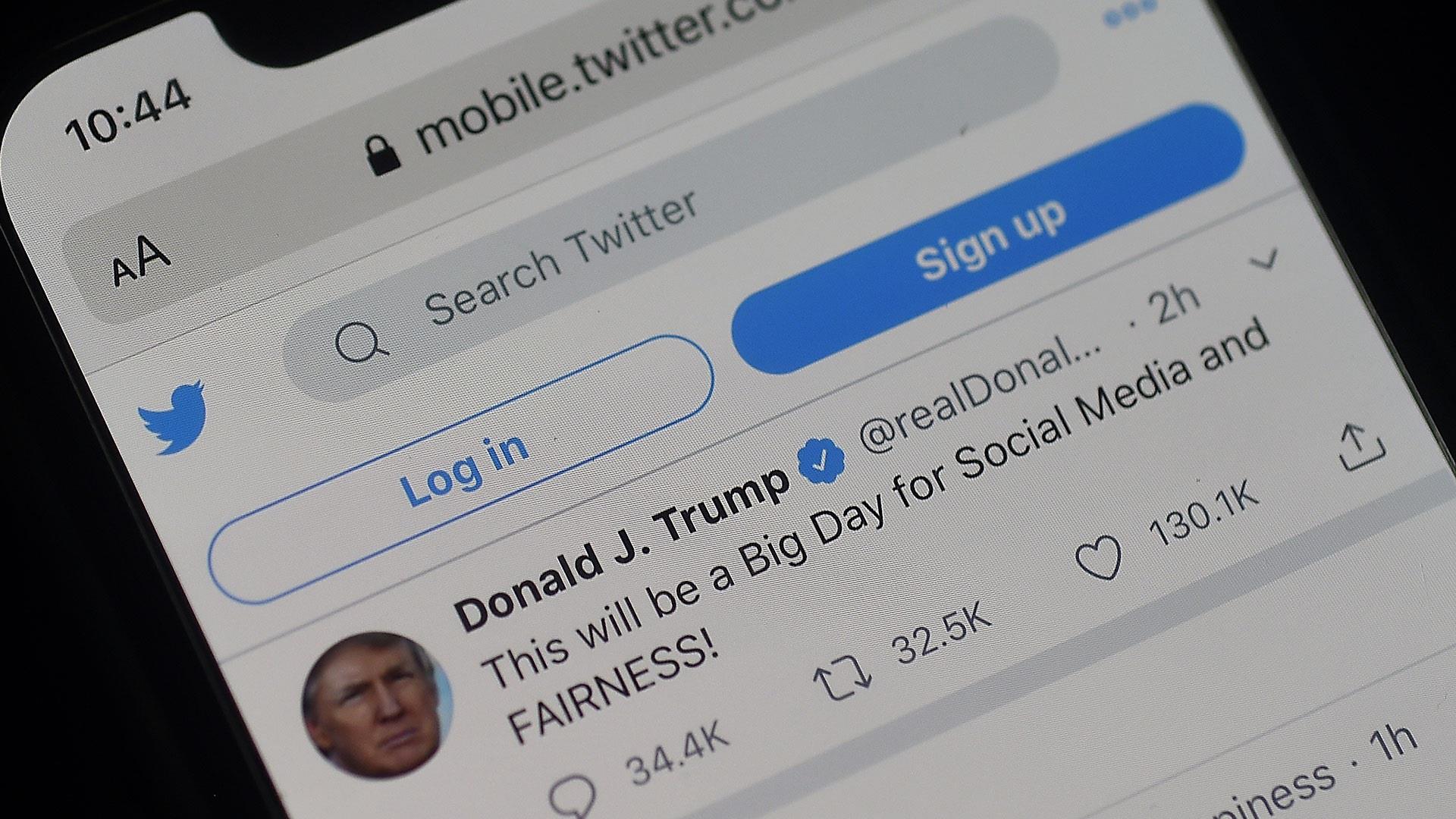
It comes two days after Twitter added a "Get the facts" label to two of Trump's tweets against vote-by-mail efforts in California, calling them "fraudulent" and saying that mail boxes would be robbed.
The Twitter label linked to a "fact check" page with news reports and information refuting Trump's claims.
On Wednesday Trump responded on Twitter:
"Republicans feel that Social Media Platforms totally silence conservatives voices. We will strongly regulate, or close them down, before we can ever allow this to happen. We saw what they attempted to do, and failed, in 2016. We can't let a more sophisticated version of that....
....happen again. Just like we can't let large scale Mail-In Ballots take root in our Country. It would be a free for all on cheating, forgery and the theft of Ballots. Whoever cheated the most would win. Likewise, Social Media. Clean up your act, NOW!!!!"
Leaked versions of the text of the executive order reported by several media companies show that it will ask the independent Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to look into rewriting the liability protections that social media companies currently have.
Currently, under Section 230 of the federal Communications Decency Act, internet platforms are protected from lawsuits -- unlike newspapers and television stations that act as publishers and can be sued over content.
The protections were put in place in 1996 to allow the internet to grow without fears of lawsuits over what is posted online.
In Section 230, not only are internet platforms protected for what they allow online, they are also protected from what they restrict as well.
Many platforms will delete obscene, violent, or harassing content for example.
Trump's executive order claims that interventions like Twitter's fact check label amount to censorship and show that Twitter is acting as a publisher and not a platform.
The order directs the Commerce Secretary to ask the FCC for regulation clarifying the conditions under which platforms can or cannot censor content.
The order also says it would ask all federal agencies to review how much advertising money is spent on social media platforms and if they have faced censorship.
The order will also collect complaints of online censorship against these platforms and send them to the Department of Justice and the Federal Trade Commission to consider action.
Finally the order asks the Attorney General to create a working group with attorneys from each state to examine what state laws are available to enforce that platforms are complying with the law.
The executive order will likely face legal challenges and would probably need congressional approval, First Amendment expert Jack Balkin told The Washington Post.
Additionally, the FCC and the FTC are independent agencies that do not answer to the White House. It is up to each agency to decide if they will act on Trump's request.
Two members of the FCC, one Democrat and one Republican, have already offered opposing views on the executive order.
Twitter and Facebook issued dozens of new rules to avoid a repeat of the false postings about candidates and the voting process that marred the 2016 election, the AP reported.
Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg criticized Twitter's latest fact check move on Fox News, saying that privately-owned digital platforms shouldn't act at as the "arbiter of truth" for everything posted online.
This caused a social media tiff as Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey later tweeted:
"We'll continue to point out incorrect or disputed information about elections globally... This does not make us an 'arbiter of truth.' Our intention is to connect the dots of conflicting statements and show the information in dispute so people can judge for themselves."